Introduction
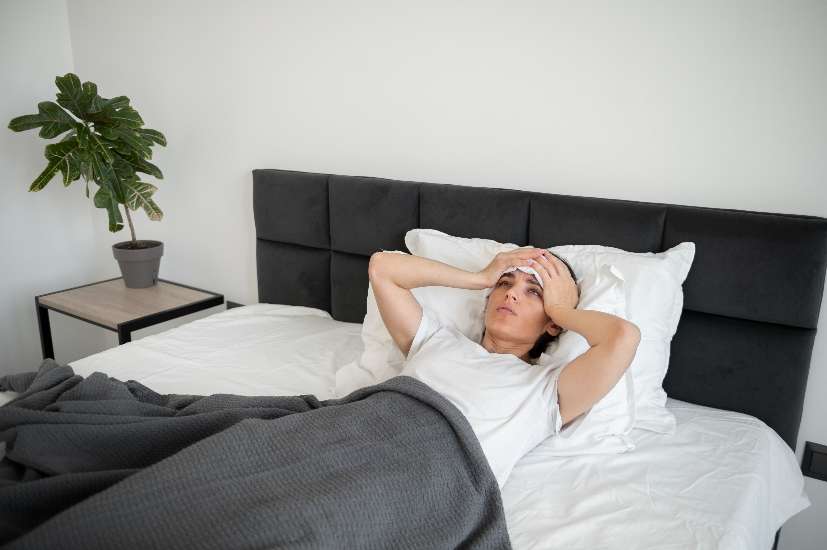
Extreme migraine pain is a debilitating condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by intense headaches, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound, migraines can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Understanding what migraines are, their types, causes, symptoms, treatments, and home remedies can help those suffering from extreme migraine pain manage their condition more effectively. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of migraines, with a particular focus on extreme migraine pain. Migraines affect 6 million people in the UK. Identifying and avoiding the things that trigger migraines is an important part of managing them, says Dr Dawn Harper.
What is Extreme Migraine Pain?
Migraine is a neurological condition that causes recurring headaches ranging from moderate to severe intensity. These headaches typically affect one side of the head and are often accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. Extreme migraine pain refers to the severe end of the spectrum, where the pain can be so intense that it interferes with daily activities, making it difficult to work, socialize, or even perform basic tasks.
Types of Migraines
Migraines are classified into several types, each with its unique characteristics. Understanding the different types can help in identifying the specific kind of migraine a person may be experiencing.
1. Migraine with Aura
A migraine with aura is characterized by visual disturbances or other neurological symptoms that precede the headache. These symptoms may include flashing lights, blind spots, or tingling sensations in the face or limbs. The aura typically lasts for about 20-60 minutes before the headache begins.
2. Migraine without Aura
This is the most common type of migraine, where the headache occurs without any preceding neurological symptoms. The pain is usually on one side of the head and can last from a few hours to several days.
3. Chronic Migraine
Chronic migraine is defined as having headaches on 15 or more days per month, with at least eight of those days being migraine headaches. This condition is particularly debilitating, as the frequency and intensity of the pain can lead to significant impairment in daily functioning.
4. Hemiplegic Migraine
Hemiplegic migraine is a rare and severe type of migraine that causes temporary paralysis on one side of the body. This type of migraine can be frightening, as it mimics the symptoms of a stroke. The paralysis usually resolves within 24 hours but may last longer in some cases.
5. Vestibular Migraine
Vestibular migraines are associated with dizziness, vertigo, and balance problems. The headache may or may not be present, but the dizziness can be severe enough to cause nausea and vomiting.
Causes of Extreme Migraine Pain
The exact cause of migraines is not fully understood, but several factors are known to contribute to the development of extreme migraine pain. These factors can vary from person to person, and in many cases, multiple triggers may be involved.
1. Genetic Predisposition
Migraines often run in families, suggesting a genetic component to the condition. If one or both parents suffer from migraines, there is a higher likelihood that their children will also experience them.
2. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in women, are a common trigger for migraines. Many women experience migraines related to their menstrual cycle, pregnancy, or menopause. Hormonal medications, such as birth control pills, can also trigger or worsen migraines.
3. Stress and Mental Health
Stress is a significant trigger for migraines, and those who experience high levels of stress are more likely to suffer from extreme migraine pain. Mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression can also exacerbate migraine symptoms, creating a cycle of pain and emotional distress.
4. Environmental Factors
Environmental factors such as changes in weather, strong smells, bright lights, and loud noises can trigger migraines in susceptible individuals. Travel, altitude changes, and exposure to smoke or pollution are also known triggers.
5. Dietary Triggers
Certain foods and beverages are known to trigger migraines in some individuals. Common dietary triggers include aged cheeses, processed meats, alcohol (especially red wine), caffeine, and artificial sweeteners. Skipping meals or fasting can also trigger migraines.
Symptoms of Extreme Migraine Pain
Extreme migraine pain is not just a severe headache; it is often accompanied by a range of symptoms that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Understanding these symptoms can help in recognizing and managing migraines more effectively.
1. Intense Headache
The hallmark symptom of extreme migraine pain is a throbbing or pulsating headache, typically on one side of the head. The pain can range from moderate to severe and is often described as debilitating.
2. Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea is a common symptom of migraines, and in severe cases, it can lead to vomiting. The nausea may be triggered by the headache itself or by sensitivity to light, sound, or smell.
3. Sensitivity to Light and Sound
Many individuals with extreme migraine pain experience heightened sensitivity to light (photophobia) and sound (phonophobia). This sensitivity can make it difficult to be in brightly lit or noisy environments during a migraine attack.
4. Visual Disturbances
As mentioned earlier, migraines with aura are characterized by visual disturbances such as flashing lights, blind spots, or zigzag patterns. These visual symptoms typically occur before the headache begins.
5. Fatigue and Weakness
Migraines can leave individuals feeling extremely fatigued and weak, both during and after the attack. This fatigue can last for several hours or even days, making it difficult to resume normal activities.
Treatments for Extreme Migraine Pain
Managing extreme migraine pain often requires a combination of treatments tailored to the individual’s specific needs. Treatment options may include medication, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies.
1. Medication
Several medications are available to treat migraines, including:
- Over-the-counter Pain Relievers
- Medications such as ibuprofen, aspirin, or acetaminophen can help relieve mild to moderate migraine pain.
- Triptans
- Prescription medications like sumatriptan and rizatriptan are specifically designed to treat migraines. They work by narrowing blood vessels and blocking pain pathways in the brain.
- Ergotamines
- These medications, such as ergotamine and dihydroergotamine, are used to treat migraines by constricting blood vessels. They are often used for migraines that don’t respond to triptans.
- Preventive Medications
- For individuals with chronic migraines, preventive medications such as beta-blockers, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants may be prescribed to reduce the frequency and severity of attacks.
2. Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can help reduce the frequency and severity of extreme migraine pain:
- Stress Management
- Since stress is a major trigger for migraines, finding effective ways to manage stress is crucial. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can be beneficial.
- Regular Sleep Schedule
- Maintaining a consistent sleep routine can help prevent migraines triggered by sleep disturbances.
- Dietary Modifications
- Identifying and avoiding dietary triggers, such as caffeine, alcohol, and processed foods, can reduce the likelihood of a migraine attack.
- Exercise
- Regular physical activity can help improve overall health and reduce stress, which may help prevent migraines.
3. Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, several home remedies can provide relief from extreme migraine pain:
- Cold or Hot Compresses
- Applying a cold or hot compress to the head or neck can help alleviate migraine pain.
- Hydration
- Dehydration is a common trigger for migraines, so staying well-hydrated is essential.
- Essential Oils
- Some individuals find relief from migraines by using essential oils such as peppermint or lavender oil, which can be applied to the temples or inhaled.
- Relaxation Techniques
- Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce the intensity of migraine pain.
Conclusion
Extreme migraine pain is a complex and debilitating condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Understanding the causes, types, symptoms, and treatments of migraines is essential for managing this condition effectively. While medication and lifestyle changes play a crucial role in preventing and treating migraines, home remedies and stress management techniques can also provide valuable relief. By taking a comprehensive approach to managing extreme migraine pain, individuals can improve their overall well-being and reduce the frequency and severity of their migraine attacks. Remember, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.